The Benefits of Fermented & Cultured Foods
Cultured and fermented foods are rich in beneficial bacteria, also called probiotics, which aid digestive “gut” health. Making your own yogurt, kombucha, tempeh, natto, and more at home is also economical. Homemade yogurt costs about one third the price of store-bought; and fermentation preserves foods, which reduces food waste and saves you money.
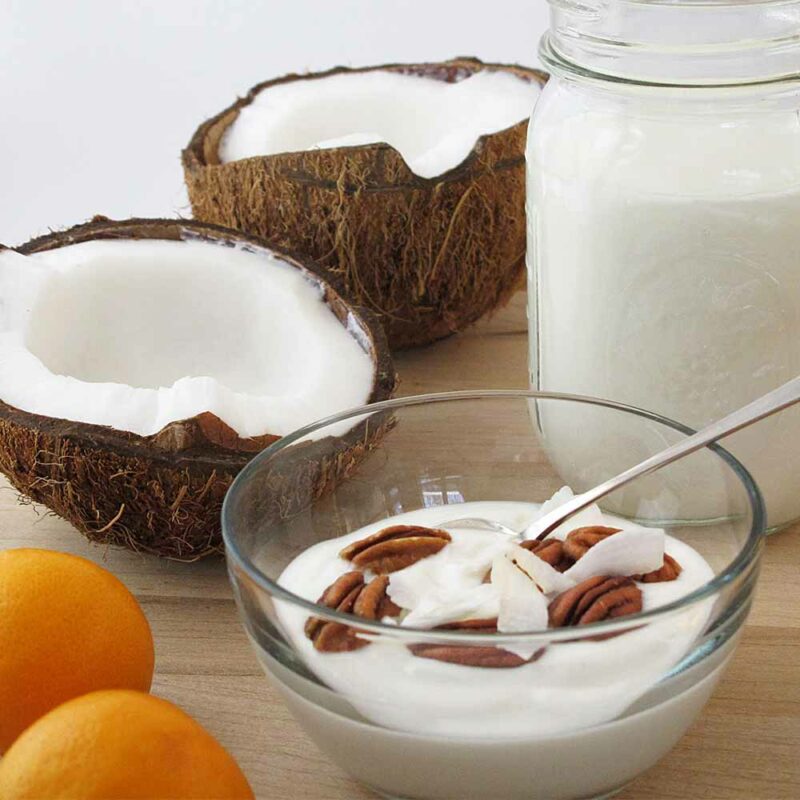
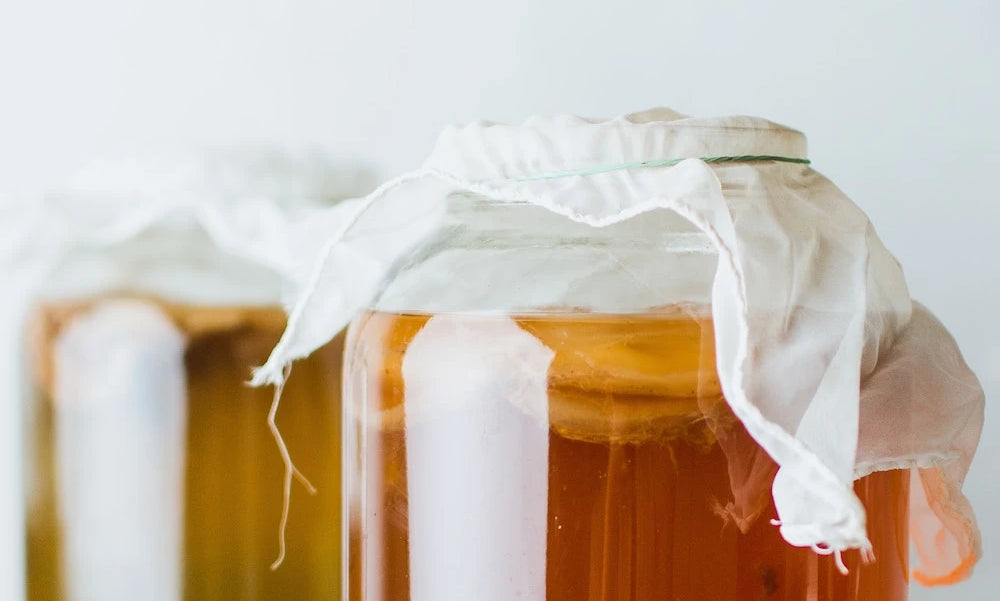


Fermentation vs. Culturing
Fermentation breaks down nutrients in food, making them easier to digest. This process can happen with or without the use of cultures. Cultures—microorganisms like bacteria and yeast—are used to kick-start the fermentation process. Therefore, cultured food refers to foods that have been fermented using a starter culture. Both fermented and cultured foods are made with microorganisms, but not all fermented foods are cultured foods or probiotics.









 Select Country
Select Country